|
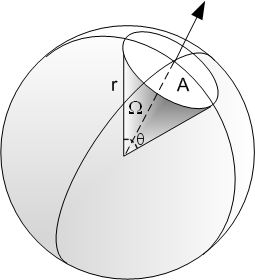
A solid angle is similar in 3 dimensions to a plane angle in 2 dimensions.
A solid angle Ω is equal to the ratio of the viewed surface A divided by the square of the viewed distance r.
Ω=A/r^2
It is expressed in steradian (sr), the official SI unit - international system of units. It is comprised of numbers between 0 and 4π sr for a whole sphere.
For a regular cones, solid angle Ω is equal to Ω =2 π x (1 - cos(θ/2))
where θ is the plane angle of a cone apex. For example, a hemisphère (half ball) has a plan angle θ of π rd and a solid angle of 2π sr
If we reverse the previous formula, we can deduct the plane angle θ from the solid angle Ω :
θ = 2 x arccos(1- Ω/2π)
For example, the apparent diameter of the moon seen from earth is θ=0.5 °, which is equivalent to a solid angle of about 6e-5 steradian.
Reading eyes vision field is θ=3 ° (0.002 sr) (foveal zone).
The peripheral vision field of eyes is about θ=25 ° (ellipse shape with -15° left, +15 ° right, -8° high, +12° low) so about 0.15 sr.
The following field is a solid angle Ω of a regular cone whose plane angle θ is indicated on the top array in any unit (like degrees).
|


 Unit Converters Home Page
Unit Converters Home Page Length converter
Length converter Weight converter
Weight converter Speed converter
Speed converter Temperature converter
Temperature converter Duration converter
Duration converter Pressure converter
Pressure converter IBAN Computer
IBAN Computer Firewood
Firewood Decoding French Social Security Number
Decoding French Social Security Number Currency converter
Currency converter Area converter
Area converter Inflation calculator
Inflation calculator Volume converter
Volume converter Life expectancy
Life expectancy Power converter
Power converter Body Mass Index calculator
Body Mass Index calculator Pentagon
Pentagon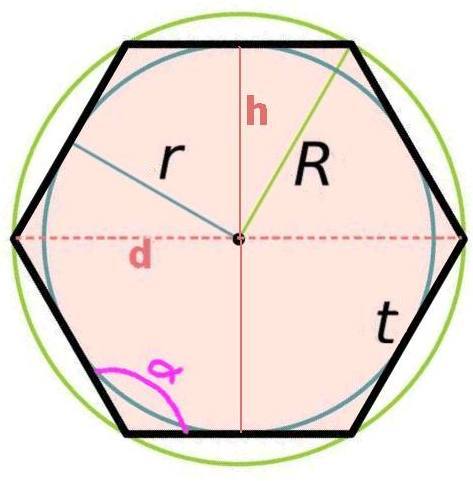 Hexagon
Hexagon Heptagon
Heptagon Octagon
Octagon English quiz
English quiz Historical Currency Converter
Historical Currency Converter  Historical rates graph
Historical rates graph Sokoban Solver
Sokoban Solver